On-page SEO is a set of best practices used to optimise everything that appears within the HTML of your page to rank higher on search engines. These could include optimising meta data, page headers, on-page body content (E-A-T signals) and images. Unlike Technical SEO or Off-Page SEO, On-Page SEO helps search engines understand the relevance of your webpage content for your target keywords.
On-Page SEO Checklist & Best Practice Guide
In this post, I am sharing On-Page SEO best practices that you can apply on your site pages. Focus on what will make an impact on the site.
Optimise Title Tags, Meta Descriptions & Page Headings
Page titles are an important element of your site pages and one of the most important factors of on-page SEO. The Title tag tells the visitors and search engines what content they can expect from the web page. They’re placed in the head section of your page within the <title> tag. As a best practice, every indexable page of your site must have a unique page title targeting relevant terms relevant to the page content.
Meta Descriptions are snippets that summarise the content of the webpage and appear on the SERPs below the page title. They’re placed in the head section of your page within the <meta name=”description” content=”your meta description” />. Unlike page titles, they are not a direct ranking factor. An enticing meta description can increase CTR to your website from the SERPs. As a best practice, every indexable page of your site must have a unique meta description accurately reflecting the page to entice users to click on it when it appears within SERPs.
Heading tags are used to structure your page content. The main heading is often a <h1> heading that defines the content of the page. Use at most one <h1> per page. It’s best practice to include your primary keyword in the <H1> header and ensure it is relevant to the content that is in place on the page. Other forms of headings include <h2>, and <h3> used as sub-headings for the various sections of your page. Google uses headings to understand different parts of a page for context.
When it comes to meta data and page headers, I would review the following;
- Check if any of your indexable pages are missing page titles, meta descriptions or H1s.
- Check if there is a duplication of page titles & meta descriptions.
- Check the relevancy and lengths of your page titles & meta descriptions.
- Check if there are multiple page titles or meta descriptions defined within the source code.
Follow this link for best practices for page titles, meta descriptions and headings.
Since 2021, Google can also rewrite page titles and meta descriptions if they feel it’s important or appropriate to better match that query.
Create High-Quality Content – E-A-T
Creating high-quality content is crucial for achieving topical authority and driving organic traffic to your website. To establish yourself as an expert on a topic, your site needs to comprehensively cover it, and your content must be of high quality. This is where E-A-T (Expertise, Authority, Trustworthiness) comes in.
To ensure your content has high E-A-T, get quotes from authoritative sources in your niche. Take the time to understand content structure before writing and group sub-sections correctly. Use statistics to back up claims to earn the trust of your audience.
Long-tail keyword research and manual SERP analysis can reveal opportunities for ranking. Writing semantic-rich content that fulfils search intent and provides a great reading experience can also increase E-A-T.
Remember, more entities in your content can lead to ranking for secondary keywords, further increasing your topical authority. By prioritising E-A-T in your content creation process, you can produce high-quality content that earns the trust and loyalty of your audience, leading to long-term success. I have shared my approach to creating buying guides for eCommerce here. Also, check out my how-to guide to performing an effective content audit.
Implementing author pages with descriptions can demonstrate expertise and establish authority across the site by indicating that the content is written by experts. You can also boost the site’s E-A-T by including easily discoverable contact information on a dedicated “Contact Us” page and linking it from the website’s footer.
Fix Thin Content / Low-Quality Content Issues Sitewide
Before you get around to finding and fixing low-quality thin content pages, it’s important to understand what is the difference between Good content and Thin content. Good content involves drafting in-depth, informative content that is useful for the users and of high value. Pages with good content would organically get backlinks. Undertaking keyword research to find target keywords to optimise these pages is typically the first step to on-page SEO.
Thin content on the other hand, also referred to as low-quality content is pages of your site with content that offers little to no value to the user. If your content is not valuable or trustworthy for the user, it will not offer any value to Google as well. Google likes pages with unique, valuable content that provides a good user experience.
According to Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines, if your content lacks EAT (Expertise, Authority, and Trust), it will be considered a low-quality site and impact rankings.
Google considers the following pages as low-quality as they don’t offer any value to the users and lead to poor search performance;
- Pages with automatically generated content / heavy usage of templated content.
- Thin affiliate pages.
- Pages with scraped or duplicated content.
- Spammy & Keyword stuffed page content.
- Doorway pages.
- Pages with lots of spammy or low-quality ads.
- Pages with lots of pop-ups – intrusive dialogs and interstitials that make it hard for Google and other search engines to actually understand your content.
- Poorly written content with too many grammatical & spelling mistakes.
SEO tools like Screaming Frog, Botify etc make it easy to identify content quality issues such as Thin or duplicated Content. On Screaming Frog, when the crawl is complete, you can navigate to the Content -> Low Content Pages section. On Botify there is a dedicated, content section. If you are a Sitebulb user, you can find the content report within their On-Page section (SEO -> OnPage -> Content).
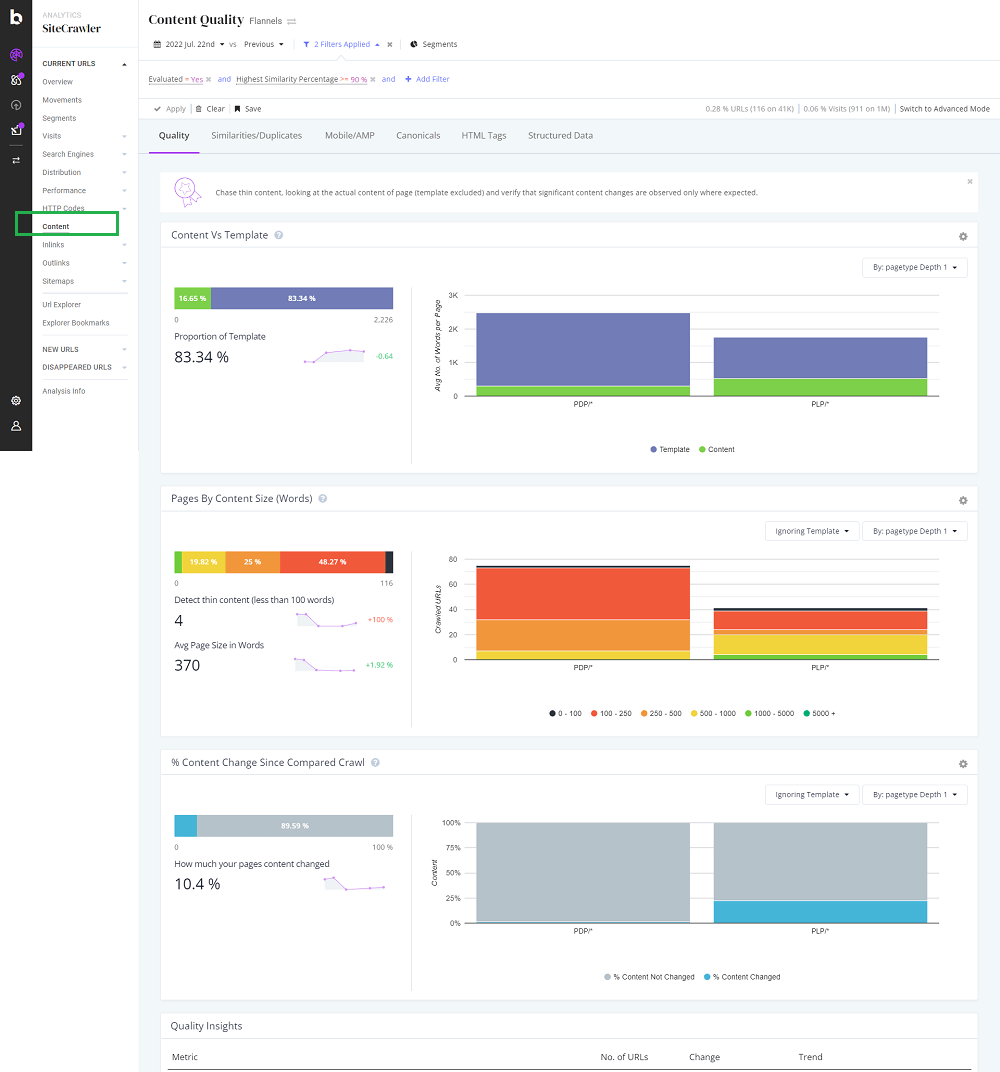
The goal is to have a website with valuable content for users. If content can’t be added to pages with thin content, consider implementing the NoIndex tag to prevent those thin pages from appearing in SERPs.
Fix Duplicate Content Issues
Duplicate content as the name suggests is an issue when the same content appears in multiple locations. Duplication would be considered as pages that are low-quality and can limit the visibility of those pages in the Google index. Google would be less inclined to crawl sites if it finds too many pages with duplicate content. It can either be internal duplication or external duplication.
Internal Site Duplication Issues
This can happen within your website when content is duplicated across pages of your own site. I have listed the most common reasons that can cause internal page duplication on sites;
- Poorly handled parameters could cause page duplication with the non-parametrised version.
- HTTP vs HTTPS versions of the same pages may cause duplication if both are indexable.
- PDFs containing the same content as your HTML content can cause duplication.
- Trailing and non-trailing slash versions of URLs can be duplicates of each other if they are both crawlable and indexable.
- Different case URLs if not handled properly via canonical or redirects can cause duplicates if the mix of lower and uppercase URLs are both crawlable and indexable.
To find internal site duplication issues, use the site:domain.com command on Google with a snippet of content from one of your site pages enclosed within quotes. If multiple pages appear within the SERP for exactly the same snippet of text, this means it’s a duplication issue and needs to be fixed. You can also use site crawlers like Screaming Frog, Botify or Sitebulb. On Screaming Frog, you need to enable near-duplicates, in your content configuration settings. Botify also has a dedicated content section to spot near internal duplicates within your site.
External Site Duplication Issues
This can happen when a website has copied content from another website. Google is generally smart in understanding who the original owner of the content is and ranking the original owner’s site pages higher in the SERPs. However, if a duplicated site is performing above the original site, the website owner can file a DMCA takedown request.
One of the most common scenarios where external duplication is common is on eCommerce product pages with non-original content. Many eCommerce sites tend to use manufacturer product descriptions due to internal copywriter resource issues or just the scale due to a large inventory. There are steps you can take to minimise a duplication penalty;
Add additional content to the duplicated product pages that provide additional value to the user. Things like linking to Similar products, adding a customer Q&As section, product FAQs, customer reviews and personalised content can help.

Meta Robots noindex Tag
The meta robots tag (<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex” />) is used to prevent a page from getting indexed in Google. In addition to that robot’s tag in place in the HTML, you can also use the X-Robots tag to noindex parts of the website such as PDFs and is implemented within the HTTP Header Response.
Optimise Image Alt Tags
Alt text provides better image context/descriptions to search engine crawlers, helping them to index an image properly. It also displays on the page if the image fails to load, The <img> alt attribute is used to specify the alternate text for an image. As a best practice, please limit the number of characters for image alt tags to an utmost of 125 characters. Use image captions for images that require a longer description. Use target keywords when possible in your alt text.
Other On-Page SEO Checks
There may be a number of other items that may be part of your on-page SEO audit checklist;
- Check if the website has effective non-javascript navigation in place.
- Check if categories, products and landing pages use breadcrumbs.
- Check if internal linking is optimised.
- Review the homepage and landing page links to check if they link to your important categories.
- Check if categories are linking to sub-categories and products.
- Check if products are linking to the main category, related categories and related products.
- Check if all your internal links link to canonical URLs with optimal anchor text.
- Check if your pagination is implemented effectively.
- Check if the URLs are SEO-friendly and if the URL parameters are set up correctly.
- Review your page’s canonical tags or hreflangs for correctness.
- Review Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines. Are there any key areas where this site fails?
How to View the On-Page SEO Elements of a Webpage?
When you are auditing a website for on-page SEO, it is important to investigate key SEO elements such as page titles, meta description, headings, hreflang tags, meta robots tags, canonical tags, schema data, images & image alt text, body content (headers and on-page content) and more. Below I have listed the most commonly used methods;
- View the page source of the pages you want to check these elements.
- Or you can inspect the DOM on Chrome developer tools by right-clicking on a page and clicking inspect to view the rendered page source. Use the search functionality to inspect the SEO elements.
- Use browser extensions such as SEO META in 1 CLICK to check meta-data, image alt tags, canonicals, headers and other SEO elements of a page.
- You can also use website site crawlers such as ScreamingFrog / Botify / Deepcrawl / various others to check the SEO elements when auditing.
No time to deal with On-page SEO? I provide On-page SEO audit services. As a Freelance SEO consultant, my job is to crawl and gather lots of data, interpret the data and provide actionable recommendations. Contact me today to discuss how I could help.
